How compatible are ground joints?
30 de November de 2023Ground glass joints are essential components in the laboratory, used to connect different glass parts, such as test tubes and flasks, tightly and securely. The key to a sound connection lies in the compatibility of the joints. In this post, we will explore how to determine the compatibility of ground joints and explain the numbered classification.
Male and female connection
Ground, tapered joints are classified by two numbers separated by a slash. The first number is the diameter in millimetres at the top or widest point of the ground joint. The second indicates the length of the ground portion. For example, a 24/40 ground joint has a diameter of 24 mm and is 40 mm long.
The basic rule for determining whether joints are compatible is simple; if the male and female portions of a joint have different first numbers, then the two pieces are not compatible. On the other hand, if the first numbers are the same, the joints will fit together.
It is important to note that tapered male and female joints with the same diameter will connect correctly, even if the length of their ground portion differs. For example, a 24/25 tapered male joint will fit on a 24/40 tapered female joint, even though they have different lengths.
This information is vital to avoid incompatibilities in the laboratory and ensure a tight, secure seal on glass connections. It is essential to understand how ground joints are numbered in order to select the right pieces and guarantee an efficient glass assembly in scientific research and experimentation.
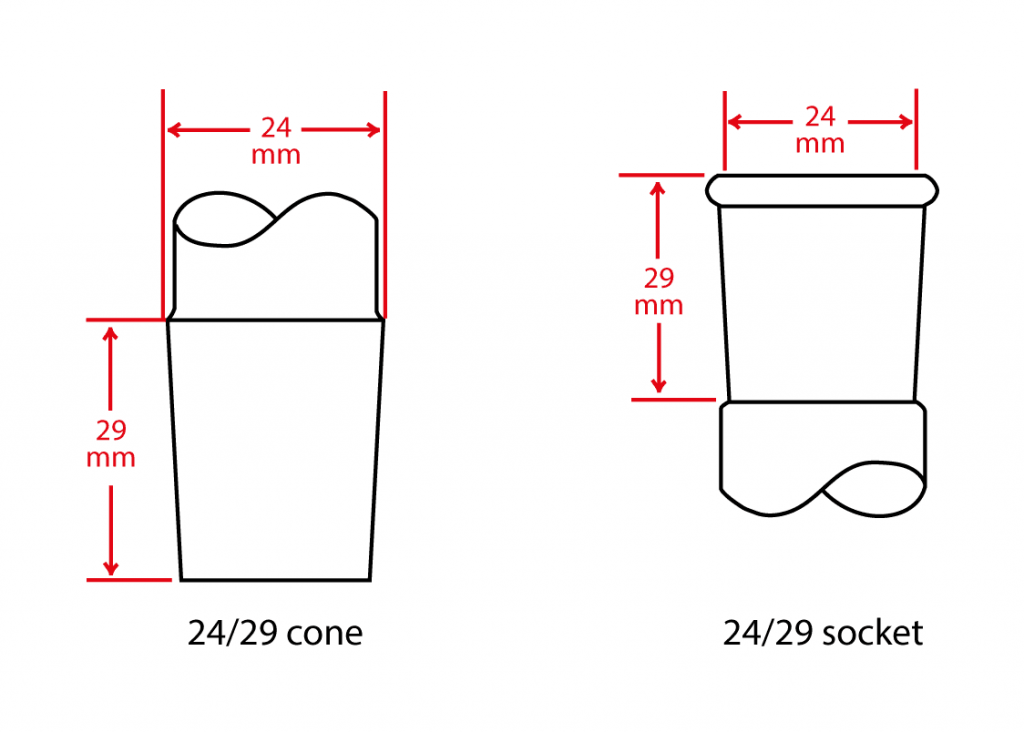
In short, the compatibility of ground glass joints depends on the two parts sharing the same number for the top diameter. This simple rule is essential to ensure safe, hermetic connections in the laboratory.
For further information or to enquire about other products or services, please write to helpdesk@scharlab.com.


